Device Services
The Automated Checkout reference implementation utilizes three device services that are used to communicate hardware event data to underlying EdgeX framework.
List of device services
- Card reader – Handles the interface between an RFID card reader and EdgeX.
- Controller board – Handles the interface between Arduino firmware and EdgeX.
- CV Inference – computer vision inference service using openVINO.
Card reader
Card reader description
The ds-card-reader device service is an EdgeX device service that allows a USB-based RFID card reader to grant access to the Automated Checkout. At a high level, this device service is responsible for discovering a specific card reader device, watching for input from that device, parsing that input, and then forwarding the input into the EdgeX framework.
There are two different modes available to this device service:
- Physical Mode: for use with a physical controller board device
- Virtual Mode: used when simulating a physical controller board by using a RESTful endpoint
The EdgeX Core services are required for the ds-card-reader to publish the card ID into the EdgeX bus (zeroMQ). Without the EdgeX core services, this device service will not function.
Card reader physical device functionality
The ds-card-reader service is much simpler than the ds-controller-board service, because it only requires mounting /dev/input:/dev/input at runtime. However, it still requires root privileges in the container at runtime so that it can interact directly with event/USB drivers.
Card reader APIs
PUT: http://localhost:48098/api/v2/device/name/card-reader/card-number
The PUT API endpoint will push the badge ID (which is sent as part of the API request body) into the card reader device service. Once the card reader device service receives the badge ID, the badge ID will be pushed into the EdgeX bus for other application services to utilize.
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"card-number":"0003278200"}' http://localhost:48098/api/v2/device/name/card-reader/card-number
Sample response:
{
"apiVersion": "v2",
"statusCode": 200
}
GET: http://localhost:48098/api/v2/device/name/card-reader/status
The GET API endpoint returns data that is not meant to be consumed for any particular purpose. When triggering this endpoint, it will execute a function (in the Go source code) called CardReaderStatus that is used as an auto-remediation mechanism to attempt to "grab" the physical card reader HID device (via evdev). If it succeeds in grabbing the underlying device, that means that the ds-card-reader device service has lost its hold on the card reader, and we need to restart the service. This endpoint is meant to be hit frequently.
curl -X GET http://localhost:48098/api/v2/device/name/card-reader/status
Sample response:
{
"apiVersion": "v2",
"statusCode": 200
}
Controller board
Controller board description
The ds-controller-board device service is responsible for handling communication with a custom-built Arduino micro-controller board (or virtual board if you don't have physical hardware). It provides functionality for reading the lock status, door status, temperature, and humidity readings, while also sending commands to the controller board to unlock the mag-lock, and display output to the LCD.
There are two different modes available for this device service:
- Physical Mode: for use with a physical controller board device
- Virtual Mode: used when simulating a physical controller board by using a RESTful endpoint
Controller board physical device functionality
When not running in simulated mode (i.e. a physical controller board device is plugged into your system), the ds-controller-board Docker container service requires /dev/ttyACM0, which is the typically the default serial port for an Arduino microcontroller.
This may change if you have multiple serial devices plugged in. Please ensure that /dev/ttyACM0 maps to the appropriate serial device if you plan to run the ds-controller-board service with a physical device.
It is important to note that the ds-controller-board service is capable of automatically finding a TTY port aside from /dev/ttyACM0. It actually looks for the vendor and product ID (VID/PID) values specified in the service's configuration. The problems arise when we have to mount the TTY port via Docker:
- mounting
/dev:/devto the container at runtime solves the problem, but creates security risks and requires--privileged=trueon the container, which is bad practice and can lead to security issues - mounting
/dev/ttyACM0:/dev/ttyACM0solves the problem, assuming there is only one serial device
Therefore, if you have multiple serial devices plugged into your system, please manually edit the docker-compose.ac.yml file to mount your /dev/ttyACM_X_ appropriately. You may want to explore creating udev rules to enforce TTY consistency.
Controller board APIs
PUT: http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/lock1
This PUT command will operate magnetic lock1. Depending on the numeric value of lock1 (boolean 0/1), the lock state will either be locked or unlocked.
Simple usage example:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"lock1":"0"}' http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/lock1
This will make the request directly to the device service itself instead of proxying through the EdgeX command API:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"lock1":"0"}' http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/lock1
PUT: http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/lock2
This PUT command will operate magnetic lock2. Depending on the numeric value of lock2 (boolean 0/1), the lock state will either be locked or unlocked.
Note
Currently lock2 has no purpose. During the initial architect/design phase of Automated Checkout, there were two locks. This was later reduced to a single mag-lock.
Sample usage:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"lock2":"1"}' http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/lock2
This will make the request directly to the device service itself instead of proxying through the EdgeX command API:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"lock2":"1"}' http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/lock2
Success
Response Status Code 200 OK.
Failure
Response Status Code 400 Bad Request
PUT: http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/displayRow0
This PUT command will operate the display (LCD) and control the text to be put on the first line of the display.
Simple usage :
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"displayRow0":"The Earth is round"}' http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/displayRow0
This will make the request directly to the device service itself instead of proxying through the EdgeX command API:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"displayRow0":"The Earth is round"}' http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/displayRow0
Info
On the endpoint URL, Change displayRow0 index to 1, 2, or 3 to display and control the text to be put on the second, third, and forth line accordingly.
Success
Response Status Code 200 OK.
Failure
Response Status Code 400 Bad Request
PUT: http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setTemperature
This PUT command will emulate the temperature sensed by the controller board as a persistent value.
Info
setTemperature is a float64. Any non-float64 value will be interpreted as '0.00' (do not have to specify decimal values).
Simple usage :
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"setTemperature":"12.00"}' http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setTemperature
This will make the request directly to the device service itself instead of proxying through the EdgeX command API:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"setTemperature":"12.00"}' http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setTemperature
Success
Response Status Code 200 OK.
Failure
Response Status Code 400 Bad Request
PUT: http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setHumidity
This PUT command will emulate the humidity sensed by the controller board as a persistent value.
Info
setHumidity is an integer. Any non-integer value will be interpreted as '0'.
Simple usage example:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"setHumidity":"12"}' http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setHumidity
This will make the request directly to the device service itself instead of proxying through the EdgeX command API:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"setHumidity":"12"}' http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setHumidity
Success
Response Status Code 200 OK.
Failure
Response Status Code 400 Bad Request
PUT: http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setDoorClosed
This PUT command will emulate the "door-closed" state sensed by the controller board as a persistent value.
Info
setDoorClosed is a boolean-integer. Any non-boolean-integer value will be interpreted as '0' (and thus 'false'). Only '1' will result in 'true'.
Simple usage example:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"setDoorClosed":"0"}' http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setDoorClosed
This will make the request directly to the device service itself instead of proxying through the EdgeX command API:
curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"setDoorClosed":"0"}' http://localhost:48097/api/v2/device/name/controller-board/setDoorClosed
Success
Response Status Code 200 OK.
Failure
Response Status Code 400 Bad Request
CV inference
CV inference description
The ds-cv-inference contains the following components:
- A golang implementation using openVINO inference engine and openVINO product detection model. This application uses preloaded images as an input to calculate inventory deltas. The images contain some products supported by the model and are used to simulate a purchase or stocking the cooler. The openVINO product detection model is intended for demo purposes. For production environment, please replace it with your own model.
- The preloaded images are used in sequence to simulate a purchase using a circular queue to loop through them.
- An EdgeX MQTT device service that converts MQTT messages into EdgeX event readings
The following picture illustrates the flow to calculate the inventory deltas between two preloaded images:
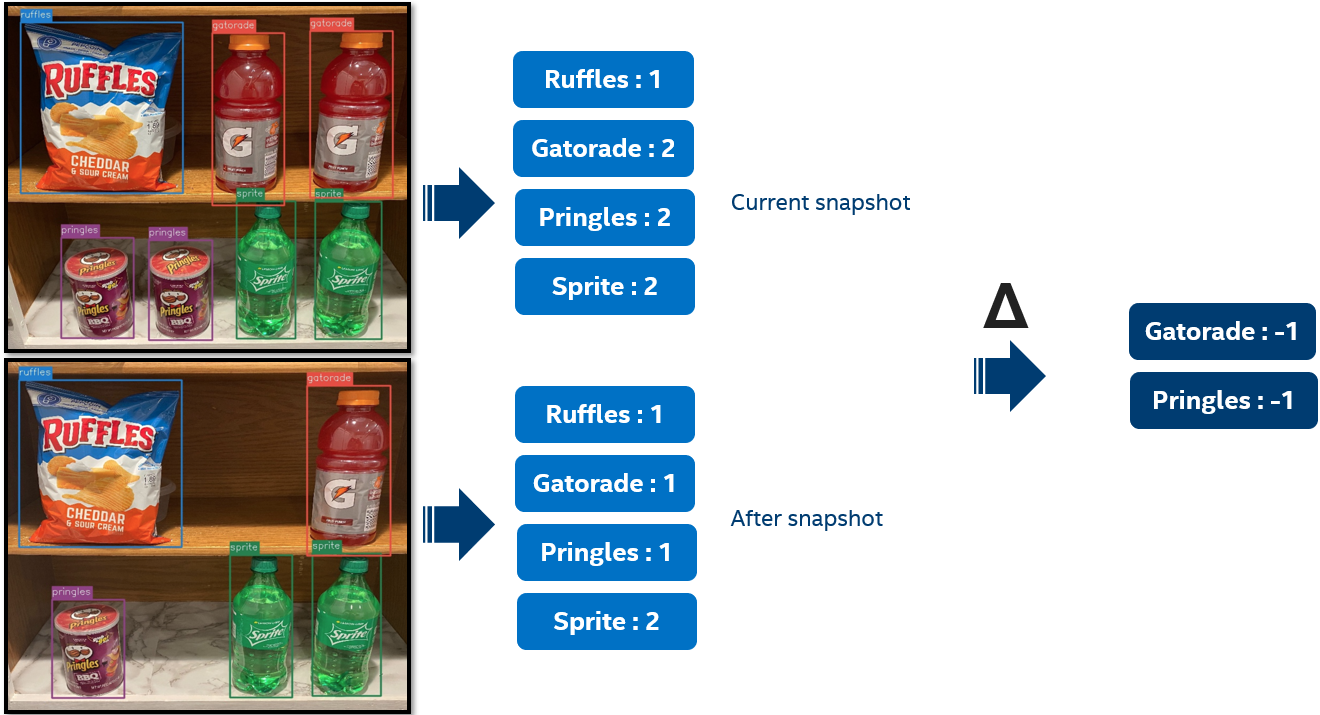
The Automated Checkout architecture uses three MQTT topics:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Inference/CommandTopic | All events pushed from EdgeX's command API are fed into this topic. The as-vending and as-controller-board-status are two services that make requests to this API, typically for making door close/open and heartbeat events. |
| Inference/ResponseTopic | The Automated Checkout cv inference service will respond to published messages on the Inference/CommandTopic topic on the Inference/ResponseTopic topic. |
| Inference/DataTopic | The cv inference service publishes delta SKUs on this topic, then the MQTT device service converts them into EdgeX event readings, and finally the as-vending service processes the event readings and pushes them to downstream services. |
CV inference APIs
GET: http://localhost:59982/api/v2/device/name/Inference-device/inferenceHeartbeat
The GET call to the EdgeX MQTT device service's inferenceHearbeat command will act as a health-check for the Automated Checkout cv inference service. It must return 200 OK upon swiping an RFID card in order for the vending workflow to begin. If it does not, the as-vending service will enter maintenance mode.
Simple usage example:
Through EdgeX command API:
curl -X GET http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/Inference-device/inferenceHeartbeat
To MQTT device service itself:
curl -X GET http://localhost:59982/api/v2/device/name/Inference-device/inferenceHeartbeat
Sample response, 200 OK:
{
"device": "Inference-device",
"origin": 1579637607912,
"readings": [
{
"origin": 1579637607911,
"device": "Inference-device",
"name": "inferenceHeartbeat",
"value": "inferencePong"
}
]
}
PUT: http://localhost:59982/api/v2/device/name/Inference-device/inferenceDoorStatus
The PUT call to the EdgeX MQTT device service's inferenceDoorStatus command will cause the cv inference service to consume the message, and if the JSON PUT key inferenceDoorStatus has the string value "true", an inference attempt will begin. The service will subsequently respond with a message containing the inventory delta (aka SKU delta).
Simple usage example:
Through EdgeX command API:
curl -X PUT -d '{"inferenceDoorStatus":"true"}' http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/Inference-device/inferenceDoorStatus
To MQTT device service itself:
curl -X PUT -d '{"inferenceDoorStatus":"true"}' http://localhost:59982/api/v2/device/name/Inference-device/inferenceDoorStatus
Success
Response Status Code 200 OK.